Electro-optic modulator with periodic p-n junction in slow-light waveguide grating
ABSTRACT
The invention concerns an electro-optical modulator, wherein a band-edge slow light in silicon waveguide gratings is applied to Mach-Zehnder modulators based on the plasma dispersion effect, reaching improved modulation efficiency and reduced energy dissipation.
The present invention allows production of slow-light modulators for silicon photonics with reduced energy dissipation.
DESCRIPTION
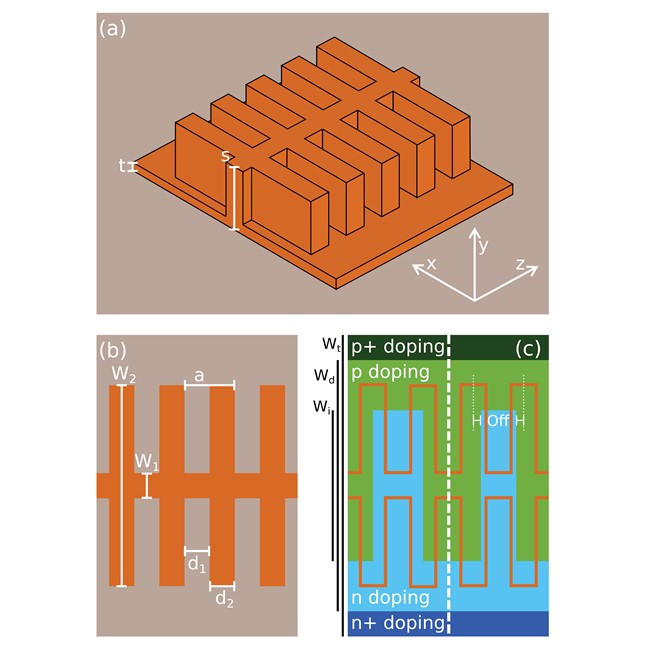
The invention is based on an interleaved p-n junction with the same periodicity as the silicon waveguide grating is used, in order to achieve optimal matching between the electromagnetic field profile and the depletion regions of the p-n junction. The resulting modulation efficiency is strongly improved as compared to common modulators based on normal rib waveguides, even in a bandwidth of 20-30 nm near the band edge, while the total insertion loss due to free carriers is not increased.
ADVANTAGES
- Strongly improved modulation efficiency in a bandwidth up to 20–30 nm
- Increased slow-light modulator bandwidth
- Reduced loss of the slow-light structure relative to a lateral p-n junction
- Improved efficiency and reduced free-carrier induced insertion losses
APPLICATIONS
- Telecommunication networks
- Electro-optical conversion of information in datacenters
INVENTORS
Lucio Andreani, Dario Gerace, Marco Passoni, John William Whelan-Curtin
KEYWORDS
Electro-optical modulators; Slow light; Interleaved p-n junction; Plasma dispersion effect
PRIORITY NUMBERS
102019000006998
APPLICANT
Università di Pavia 75% University of Cork 25%